How to install, start and test XAMPP on Mac OSX. Webucator provides instructor-led training to students throughout the US and Canada. We have trained over 90,000 students from over 16,000 organizations on technologies such as Microsoft ASP.NET, Microsoft Office, Azure, Windows, Java, Adobe, Python, SQL, JavaScript, Angular and much more. The DMG File Reader utility provides option to add multiple DMG files. Users can open Multiple DMG files one by one and read DMG file's contents of Mac OSX on Windows operating systems. Therefore, it totally depends upon the choice of users to select and view one file or multiple file at a time. Install and run Docker Desktop on Mac. Double-click Docker.dmg to open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder. Double-click Docker.app in the Applications folder to start Docker. (In the example below, the Applications folder is in “grid” view mode.). The dmg file will be the install dmg (if there’s no shared content folder, you’ve struck gold) and however, if it isn’t, navigate to shared contents and there will be an installESD.dmg and that will be the install file. I’m sure you know what to do from there.
Estimated reading time: 3 minutes
Docker Desktop for Mac is the Community version of Docker for Mac.You can download Docker Desktop for Mac from Docker Hub.
By downloading Docker Desktop, you agree to the terms of the Docker Software End User License Agreement and the Docker Data Processing Agreement.
System requirements

Your Mac must meet the following requirements to successfully install Docker Desktop:
macOS must be version 10.14 or newer. That is, Mojave, Catalina, or Big Sur. We recommend upgrading to the latest version of macOS.
If you experience any issues after upgrading your macOS to version 10.15, you must install the latest version of Docker Desktop to be compatible with this version of macOS.
Note
Docker supports Docker Desktop on the most recent versions of macOS. That is, the current release of macOS and the previous two releases. As new major versions of macOS are made generally available, Docker stops supporting the oldest version and supports the newest version of macOS (in addition to the previous two releases). Docker Desktop currently supports macOS Mojave, macOS Catalina, and macOS Big Sur.
At least 4 GB of RAM.
VirtualBox prior to version 4.3.30 must not be installed as it is not compatible with Docker Desktop.
What’s included in the installer
The Docker Desktop installation includes Docker Engine, Docker CLI client, Docker Compose, Notary, Kubernetes, and Credential Helper.
Install and run Docker Desktop on Mac
Double-click
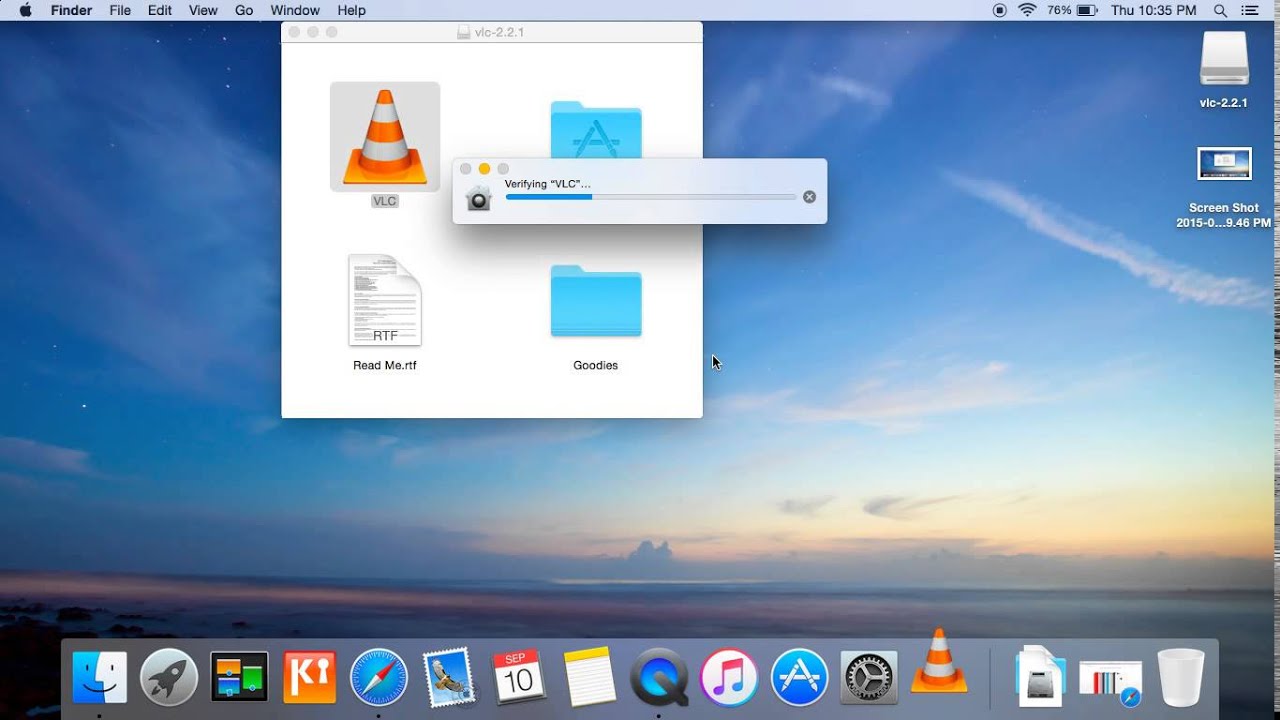
Docker.dmgto open the installer, then drag the Docker icon to the Applications folder.Double-click
Docker.appin the Applications folder to start Docker. (In the example below, the Applications folder is in “grid” view mode.)The Docker menu in the top status bar indicates that Docker Desktop is running, and accessible from a terminal.
If you’ve just installed the app, Docker Desktop launches the onboarding tutorial. The tutorial includes a simple exercise to build an example Docker image, run it as a container, push and save the image to Docker Hub.
Click the Docker menu () to seePreferences and other options.
Select About Docker to verify that you have the latest version.
Congratulations! You are now successfully running Docker Desktop.
If you would like to rerun the tutorial, go to the Docker Desktop menu and select Learn.
Automatic updates
Starting with Docker Desktop 3.0.0, updates to Docker Desktop will be available automatically as delta updates from the previous version.
When an update is available, Docker Desktop automatically downloads it to your machine and displays an icon to indicate the availability of a newer version. All you need to do now is to click Update and restart from the Docker menu. This installs the latest update and restarts Docker Desktop for the changes to take effect.
Uninstall Docker Desktop
To uninstall Docker Desktop from your Mac:
Osx Install Dmg
- From the Docker menu, select Troubleshoot and then select Uninstall.
- Click Uninstall to confirm your selection.
Important
Uninstalling Docker Desktop destroys Docker containers, images, volumes, andother Docker related data local to the machine, and removes the files generatedby the application. Refer to the back up and restore datasection to learn how to preserve important data before uninstalling.
Where to go next
- Getting started provides an overview of Docker Desktop on Mac, basic Docker command examples, how to get help or give feedback, and links to other topics about Docker Desktop on Mac.
- Troubleshooting describes common problems, workarounds, howto run and submit diagnostics, and submit issues.
- FAQs provide answers to frequently asked questions.
- Release notes lists component updates, new features, and improvements associated with Docker Desktop releases.
- Get started with Docker provides a general Docker tutorial.
- Back up and restore data provides instructionson backing up and restoring data related to Docker.
R is an incredibly powerful open source program for statistics and graphics. It can run on pretty much any computer and has a very active and friendly support community online. Graphics created by R are extremely extensible and are used in high level publications like the New York Times (as explained by this former NYT infographic designer).
RStudio is an integrated development environment (IDE) for R. It’s basically a nice front-end for R, giving you a console, a scripting window, a graphics window, and an R workspace, among other options.
R Commander is a basic graphical user interface (GUI) for R. It provides a series of menus that allow you to run lots of statistic tests and create graphics without typing a line of code. More advanced features of R aren’t accessible through R Commander, but you can use it for the majority of your statistics. (Lots of people (like me) use R Commander as a crutch for a few months before they get the hang of the R language. As intimidating as it might be to constantly type stuff at the console, it really is a lot faster.)
However, as is the case with lots of free and open source software, it can be a little tricky to install all of these different programs and get them to work nicely together. The simple instructions below explain how to get everything working right.
Mac Install Dmg File Command Line
Install R, RStudio, and R Commander in Windows
- Download R from http://cran.us.r-project.org/ (click on “Download R for Windows” > “base” > “Download R 2.x.x for Windows”)
- Install R. Leave all default settings in the installation options.
- Download RStudio from http://rstudio.org/download/desktop and install it. Leave all default settings in the installation options.
- Open RStudio.
- Go to the “Packages” tab and click on “Install Packages”. The first time you’ll do this you’ll be prompted to choose a CRAN mirror. R will download all necessary files from the server you select here. Choose the location closest to you (probably “USA CA 1” or “USA CA 2”, which are housed at UC Berkeley and UCLA, respectively).
- Start typing “Rcmdr” until you see it appear in a list. Select the first option (or finish typing Rcmdr), ensure that “Install dependencies” is checked, and click “Install”.
- Wait while all the parts of the R Commander package are installed.
- If you get permission errors while installing packages, close R Studio and reopen it with administrator privileges.
Install R, RStudio, and R Commander in Mac OS X
- Download R from http://cran.us.r-project.org/ (click on “Download R for Mac OS X” > “R-2.x.x.pkg (latest version)')
- Install R.
- Download RStudio from http://rstudio.org/download/desktop.
- Install RStudio by dragging the application icon to your Applications folder.
- Download Tcl/Tk from http://cran.r-project.org/bin/macosx/tools/ (click on
tcltk-8.x.x-x11.dmg; OS X needs this to run R Commander.) - Install Tcl/Tk.
- Go to your Applications folder and find a folder named Utilities. Verify that you have a program named “X11” there. If not, go to http://xquartz.macosforge.org/ and download and install the latest version of XQuartz.
- Open RStudio.
- Go to the “Packages” tab and click on “Install Packages”. The first time you’ll do this you’ll be prompted to choose a CRAN mirror. R will download all necessary files from the server you select here. Choose the location closest to you (probably “USA CA 1” or “USA CA 2”, which are housed at UC Berkeley and UCLA, respectively).
- Start typing “Rcmdr” until you see it appear in a list. Select the first option (or finish typing Rcmdr), ensure that “Install dependencies” is checked, and click “Install”.
- Wait while all the parts of the R Commander package are installed.
Open R Commander in Windows and OS X
Once you’ve installed R Commander, you won’t have to go through all those steps again! Running R Commander from this point on is simple—follow the instructions below.

If you decide to stop using R Commander and just stick with R, all you ever need to do is open RStudio—even simpler!

Os X Install Dmg
- Open R Studio
- In the console, type
windows()if using Windows,quartz()if using Mac OS X. (This tells R Commander to output all graphs to a new window). If you don’t do this, R Commander graphs will be output to the graphics window in RStudio. - Go to the “Packages” tab, scroll down to “Rcmdr,” and check the box to load the plugin. (Alternatively, type
library(Rcmdr)at the console.)
